Healthiest Oil to be used, a mini guide for your regular cooking:

Table of Contents
Oils available in Market
1. Vegetable Oils
- Sunflower Oil: Light and commonly used for frying and sautéing.
- Canola Oil: Neutral flavor, great for frying and baking.
- Corn Oil: Mild flavor, widely used for frying.
2. Nut and Seed Oils
- Groundnut (Peanut) Oil: Popular in Indian cooking, especially for deep frying.
- Sesame Oil: Has a distinct flavor, used in South Indian and Asian cuisines.
- Mustard Oil: Strong, pungent flavor; often used in North and East Indian cooking.
- Coconut Oil: Frequently used in South Indian cooking, particularly in Kerala cuisine.
3. Cold-Pressed Oils
- Cold-Pressed Coconut Oil: Retains natural flavor and nutrients.
- Cold-Pressed Sesame Oil: Preferred for traditional Indian dishes.
- Cold-Pressed Olive Oil: Best for raw applications like salads and light cooking.
4. Specialty Oils
- Rice Bran Oil: Light and versatile, good for frying due to its high smoke point.
- Avocado Oil: Rich in healthy fats, suitable for high-temperature cooking.
5. Olive Oils
- Extra Virgin Olive Oil: Best for raw use or low-heat cooking.
- Light Olive Oil: Has a neutral flavor, suitable for higher-heat cooking.
6. Butter and Ghee
- Ghee (Clarified Butter): Staple in Indian kitchens, enhances flavor and suitable for high-heat cooking.
7. Special Regional Oils
- Neem Oil: Used sparingly in traditional medicinal recipes, not for regular cooking.
- Safflower Oil: Commonly used in some parts of India.
Categories of Oil
1. Cold-Pressed Oils
- Extracted using mechanical pressure without applying heat.
- Retain natural nutrients, flavor, and aroma.
- Examples: Cold-pressed coconut oil, sesame oil, and mustard oil.
2. Refined Oils
- Processed to remove impurities, color, and odor.
- Often have a neutral taste and higher smoke points.
- Examples: Refined sunflower oil, refined palm oil.
3. Virgin Oils
- Extracted through mechanical means without chemicals or heat.
- Retain natural flavor, aroma, and nutrients but are not as pure as extra virgin oils.
- Examples: Virgin olive oil, virgin coconut oil.
4. Extra Virgin Oils
- The highest quality oil made from the first pressing of the oilseed or fruit.
- No heat or chemicals are used, retaining the maximum nutrients.
- Example: Extra virgin olive oil.
5. Unrefined Oils
- Minimal processing and no refining; retain natural flavors, nutrients, and aromas.
- Examples: Unrefined sesame oil, unrefined coconut oil.
6. Hydrogenated Oils
- Treated with hydrogen to solidify the oil, increasing shelf life.
- Contains trans fats, which are unhealthy.
- Example: Vanaspati (partially hydrogenated vegetable oil).
7. Expeller-Pressed Oils
- Extracted by mechanically pressing the seeds or nuts with heat generated through friction.
- May lose some nutrients compared to cold-pressed oils.
- Examples: Expeller-pressed sunflower oil, groundnut oil.
8. Blended Oils
- A mix of two or more oils, often to combine health benefits and affordability.
- Example: Rice bran oil blended with soybean oil.
9. Infused Oils
- Oils infused with herbs, spices, or other ingredients to add flavor.
- Example: Garlic-infused olive oil, chili-infused sesame oil.
10. Smoke Point-Based Categories
- High Smoke Point Oils: Suitable for frying and grilling (e.g., rice bran oil, canola oil).
- Medium Smoke Point Oils: Suitable for sautéing and stir-frying (e.g., coconut oil, mustard oil).
- Low Smoke Point Oils: Best for dressings and light cooking (e.g., extra virgin olive oil).
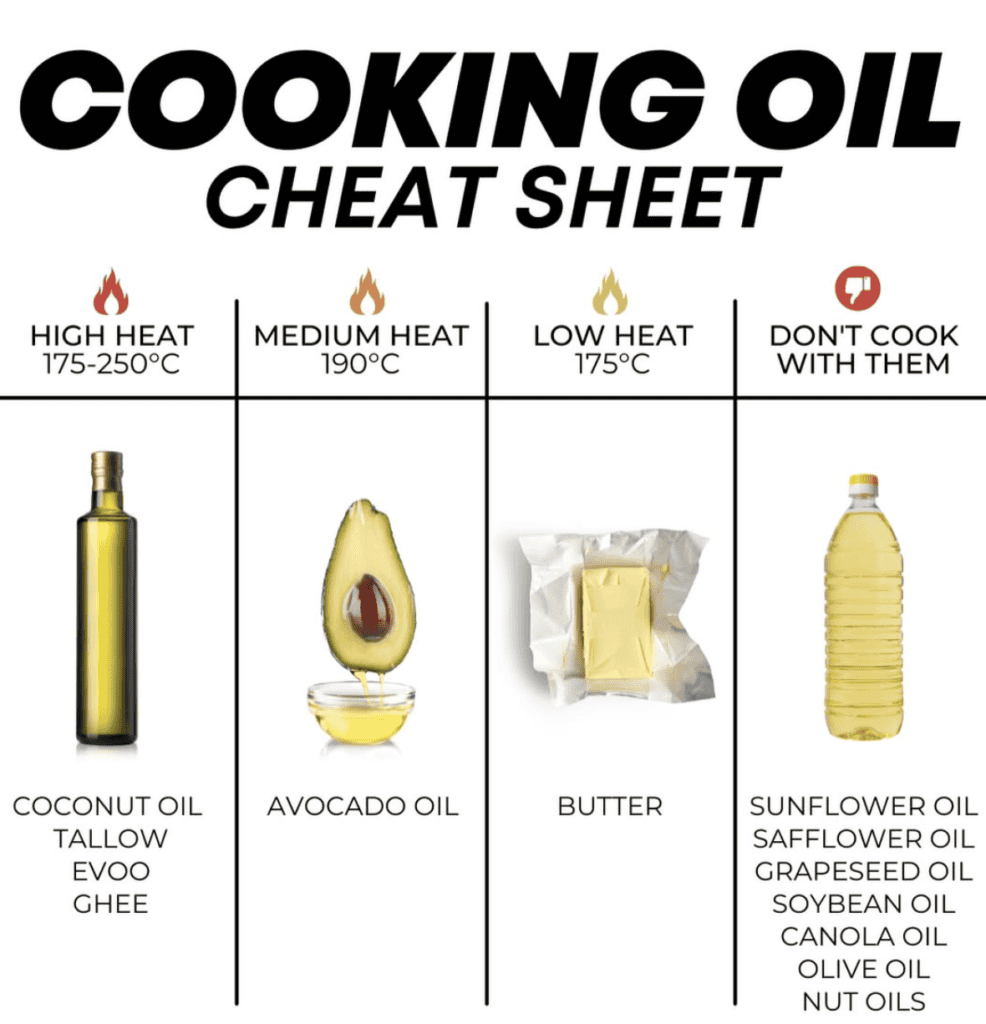
Which oil you should not be using?
Refined oils – To enhance shelf life and appearance, some refined oils contain additives and preservatives, which may have unknown long-term health effects. With the removal of nutrients during refining, these non healthy oils offer only empty calories and no significant health benefits.
Which are the Healthiest oils then?
Cold Pressed Oils or Kachi Ghaani – Cold-pressed oils retain their natural nutrients, antioxidants, and flavor, making them healthier options. They are free from chemicals and excessive heat, preserving the oil’s purity. These healthiest oils are rich in healthy fats, promoting heart health and overall well-being.